When Google releases every core algorithm update, the whole SEO industry is waiting to see what will happen next.
In this BERT algorithm, when Google states that this update is the biggest improvement in the past five years and one of the biggest rises in the overall history of search.
On the same note, this Google BERT algorithm update is going to create an impact on around 10% of English search queries in the U.S.
Yes, this is really a massive number because as we already know there are millions of searches made every day.
These things from Google’s rollout of BERT created a huge buzz in the whole SEO industry.
Are you curious to know what is BERT algorithm?
Okay, let me do it.
In this blog, I will explain what is BERT algorithm, how it works, and how it has impacted searches with examples.
Also, know how others misunderstood the Google BERT algo and Which algorithm is the precursor to BERT.
What is BERT Algorithm?
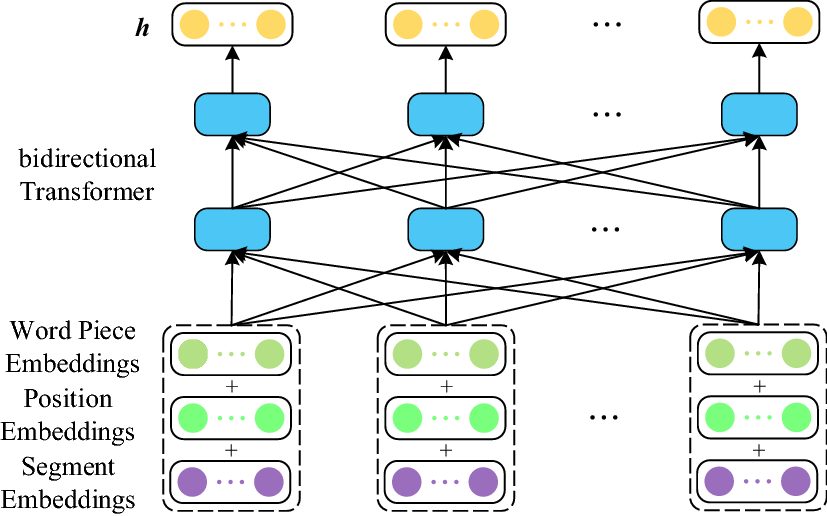
BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations for Transformers and this technique is based on a neural network for Natural Language Processing (NLP).
In simple words, the BERT algorithm is used to help Google to understand the context of the overall words in a sentence instead of processing every single word in a sentence, that Google has used before.
This BERT helps Google to provide accurate search results.
In November 2018, Google has open-sourced BERT.
What this actually means is that anyone can use BERT in AI development to train their language processing system to answer questions or perform other tasks.
The primary target of the BERT is long-tail queries or searches, where “for” and “to” are the phrases that provide various meanings in a sentence.
BERT models are applied to both search results and featured snippets. When it comes to search results, the BERT helps search better understand one in ten searches in English in the U.S.
While in other languages, BERT models are only applied to featured snippets.
And also Google has confirmed that they have been bringing BERT models for search results in more languages too.
Wondering how this will affect your search engine rankings. Find out how to track search engine rankings in a few steps.
What is a Neural Network in BERT?
The neural networks are designed to recognize the pattern by using the bidirectional context model.
In other words, neural networks in BERT are designed to know the relation between the previous and next words in a sentence to understand the context even better.
Before the initiation of BERT algorithm update, Google used only a unidirectional context model to understand the context.
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) refers to the category of artificial intelligence and is the technique of analyzing and synthesizing the natural language which is spoken by humans, this is done by training in the way how humans naturally communicate.
The Google BERT algorithm uses this NLP to understand the search query and intent more effectively to provide us with the most relevant results.
The advancement in NLP is possible because of providing bidirectional training to NLP.
How BERT Algorithm Works?
When you search for something on Google, that is long-tailed or a sentence or a query, Google’s BERT analyzes the search term with the relation between the previous and next words in the sentence using bidirectional training.
This helps Google find the overall context of the sentence and the intent behind the search.
This way BERT algorithm works to provide relevant and accurate results to the users.
For example, the word “trunk” would have the same context-free representation in “tree trunk” and “trunk of the elephant.”
Contextual models instead generate a representation of each word that is based on the other words in the sentence.
For example, in the sentence “I touched the trunk of an elephant,” a unidirectional contextual model would represent “trunk” based on “I touched the” but not “elephant.”
However, BERT represents “trunk” using both its previous and next context — “I touched the …elephant” — starting from the very bottom of a deep neural network, making it deeply bidirectional.”
Google BERT Algorithm Examples
As Google mentioned in their blog, “Particularly for longer, more conversational queries, or searches in which prepositions like ‘for’ and ‘to’ seems more important to the meaning, the Google search will be able to understand the context of the words in your query. You can search in any way that you feel natural”
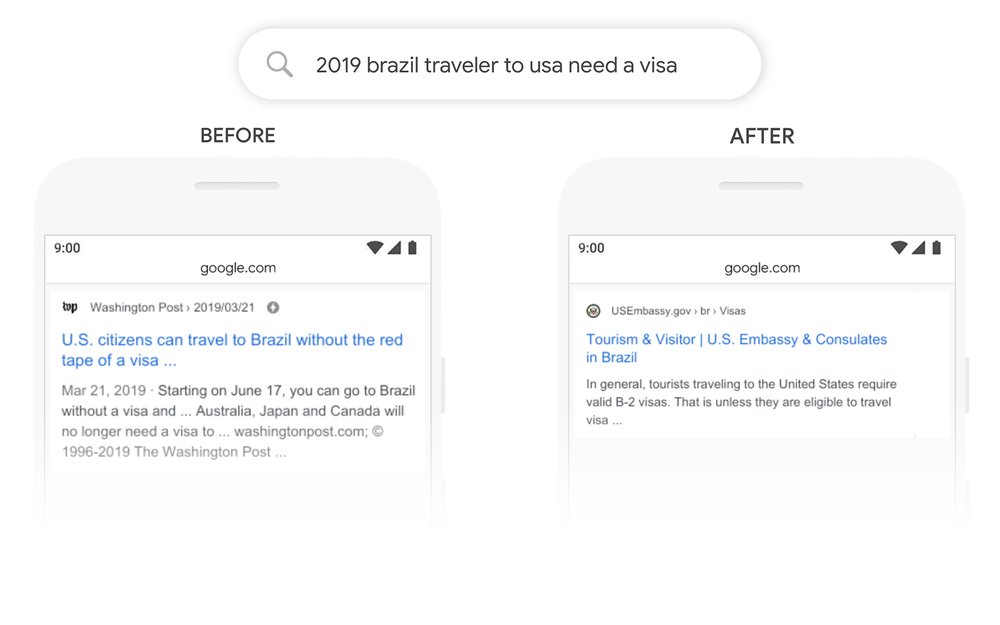
The below image depicts the search query “2019 brazil traveler to usa need a visa”. It also shows the search results before and after the Google BERT algorithm update.
The BERT finds how the preposition “to” is crucial in this search query and how it brings out the relevant results that a user would expect from this search.
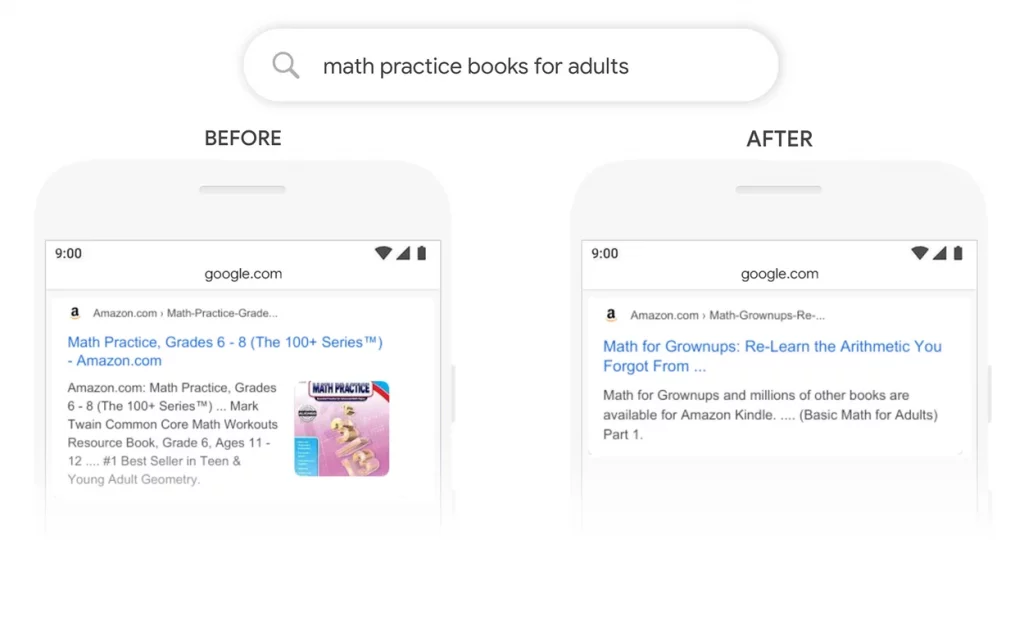
In the below example, the search query is “math practice books for adults” see how BERT helped Google to show relevant results by grasping the nuances of the language models that computers don’t understand the way how humans do.
Which Algorithm is the Precursor to BERT?
All of us heard about the RankBrain update, which was rolled out by Google in the spring of 2015 and not announced till October 26, 2015.
This RankBrain update is introduced to help Google better understand the search intent of the search query to provide relevant search results.
RankBrain understands the relationship between the words and the context of the search queries by analyzing both the content of the web page and search queries.
In the starting stage, the Rankbrain has been applied to the queries that aren’t been searched before in Google (new searches).
This means the RankBrain has applied to 15% of the google searches.
The intent of the introduction of these two algorithms, RankBrain and BERT are the same.
Also, BERT is the advancement or complementary to the RankBrain algorithm and BERT doesn’t replace RankBrain completely.
So, the RankBrain algorithm is considered the precursor to the BERT algorithm.
4 BERT Algorithm Myths
1. The Impact of BERT is Small
What do you mean by small?
Google states that the BERT algorithm update would impact one out of ten search queries in the U.S. While considering that millions of searches were made in a single day, 10% of them are not small.
2. BERT is Google’s Biggest Update of All Time
Google has mentioned in their blog, that BERT is the biggest improvement in the past five years and also BERT represents one of the biggest improvements in the history of search.
From this statement we can get, yes it is the biggest improvement but only considering the past five years when Google released the BERT (2014 – 2019) and not all time.
And also it is the biggest improvement in the history of search, but not only BERT because BERT is also the one amongst other updates.
3. BERT Gives Importance to Stop Words
When the context is influenced by the words “to”, “for”, and “from” provided as examples in the Google announcement.
Many SEOs and bloggers claim that this means stop words are more important now.
This led to many people now more often trying to include the stop words like “to”, “for”, and “from” in their contents or URLs.
4. BERT Suggests Focus on Optimizing for Long Tail Queries
“BERT Suggests Focus on Optimizing for Long Tail Queries”
This statement totally misleads everyone.
Because the BERT algorithm is to help Google to find the overall context of the search query.
This means what the users really try to find and then being able to connect that to more specific and useful information that already exists on the website.
I hope you now understand what is Google BERT algorithm update, what are the myths that go around and how BERT algorithm works.
Similarly, there are many myths spreading around various google updates. I have found 14 Google E-A-T myths that every SEOs should be aware of and understand E-A-T better.
Happy Serppling…
Published by
Sesharaja
Sesha Raja is a Product Marketer in Serpple Private Limited, an accurate rank tracker tool with many unique features. He loves to research which led him to become a content writer. He enjoys creating logical write-ups that can easily be understood by all levels of readers.
All stories by Sesharaja